Validation of a tool for estimating clinician recognition of ARDS using data from the international LUNG SAFE study
Abstract
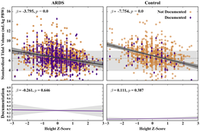
Under-recognition of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) by clinicians is an important barrier to adoption of evidence-based practices such as low tidal volume ventilation. The burden created by the COVID-19 pandemic makes it even more critical to develop scalable data-driven tools to improve ARDS recognition. The objective of this study was to validate a tool for accurately estimating clinician ARDS recognition rates using discrete clinical characteristics easily available in electronic health records. We conducted a secondary analysis of 2,705 ARDS and 1,261 non-ARDS hypoxemic patients in the international LUNG SAFE cohort. The primary outcome was validation of a tool that estimates clinician ARDS recognition rates from health record data. Secondary outcomes included the relative impact of clinical characteristics on tidal volume delivery and clinician documentation of ARDS. In both ARDS and non-ARDS patients, greater height was associated with lower standardized tidal volume (mL/kg PBW) (ARDS: adjusted ? = -4.1, 95% CI -4.5 –-3.6; non-ARDS: ? = -7.7, 95% CI -8.8 –-6.7, P<0.00009 [where ? = 0.01/111 with the Bonferroni correction]). Standardized tidal volume has already been normalized for patient height, and furthermore, height was not associated with clinician documentation of ARDS. Worsening hypoxemia was associated with both increased clinician documentation of ARDS (? = -0.074, 95% CI -0.093 –-0.056, P<0.00009) and lower standardized tidal volume (? = 1.3, 95% CI 0.94–1.6, P<0.00009) in ARDS patients. Increasing chest imaging opacities, plateau pressure, and clinician documentation of ARDS also were associated with lower tidal volume in ARDS patients. Our EHR-based data-driven approach using height, gender, ARDS documentation, and lowest standardized tidal volume yielded estimates of clinician ARDS recognition rates of 54% for mild, 63% for moderate, and 73% for severe ARDS. Our tool replicated clinician-reported ARDS recognition in the LUNG SAFE study, enabling the identification of ARDS patients at high risk of being unrecognized. Our approach can be generalized to other conditions for which there is a need to increase adoption of evidence-based care.